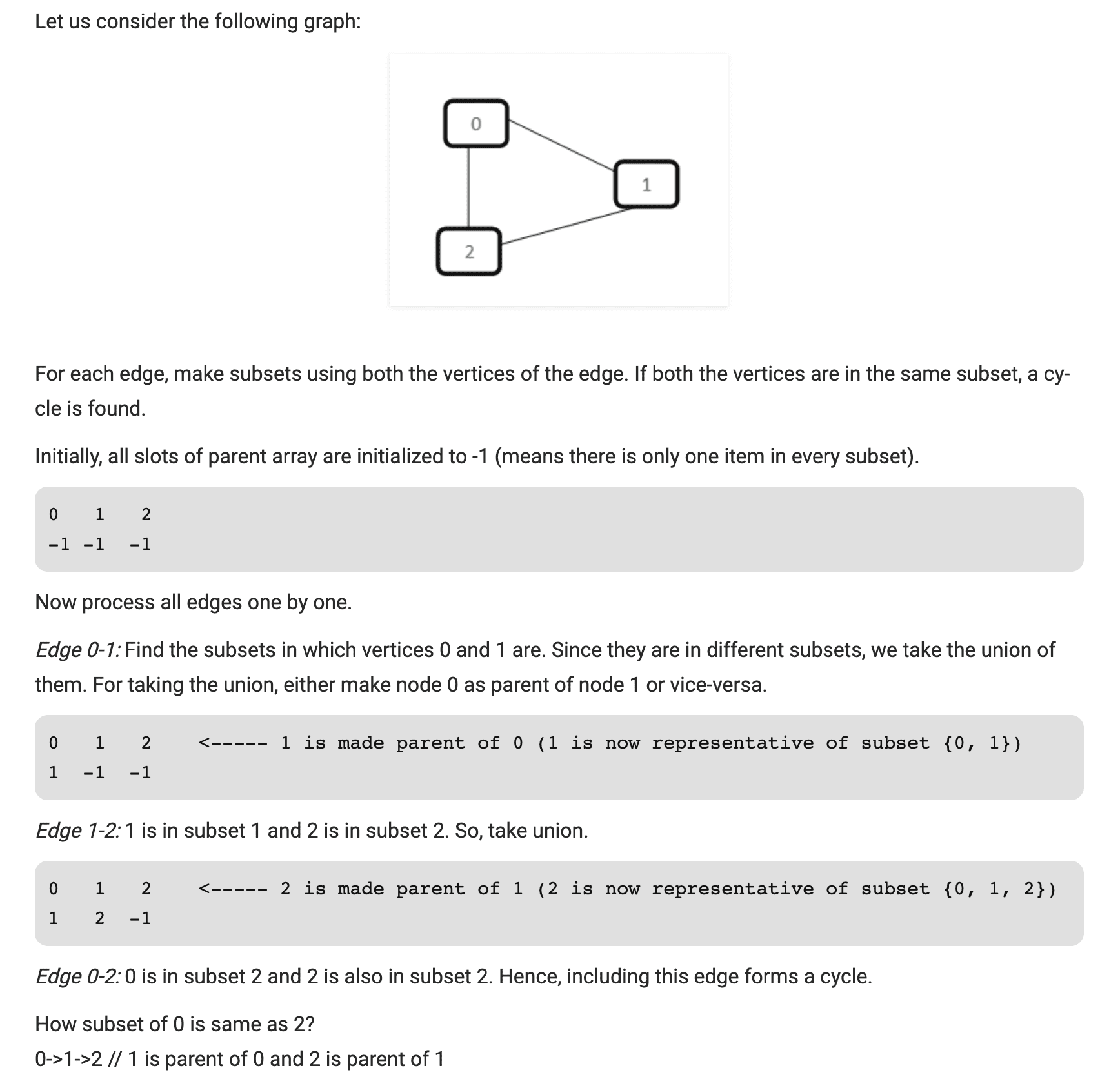
without rank and path compression, the implementation of union() and find() is naive and takes O(n) time in worst case.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80// Java Program for union-find algorithm to detect cycle in a graph
class Graph {
int V, E; // V-> no. of vertices & E->no.of edges
Edge edge[]; // /collection of all edges
class Edge {
int src, dest;
}
// Creates a graph with V vertices and E edges
Graph(int v, int e) {
V = v;
E = e;
edge = new Edge[E];
for (int i = 0; i < e; ++i)
edge[i] = new Edge();
}
// A utility function to find the subset of an element i
int find(int parent[], int i) {
if (parent[i] == -1)
return i;
return find(parent, parent[i]);
}
// A utility function to do union of two subsets
void Union(int parent[], int x, int y) {
int xset = find(parent, x);
int yset = find(parent, y);
parent[xset] = yset;
}
// The main function to check whether a given graph
// contains cycle or not
int isCycle(Graph graph) {
// Allocate memory for creating V subsets
int parent[] = new int[graph.V];
// Initialize all subsets as single element sets
for (int i = 0; i < graph.V; ++i)
parent[i] = -1;
// Iterate through all edges of graph, find subset of both
// vertices of every edge, if both subsets are same, then
// there is cycle in graph.
for (int i = 0; i < graph.E; ++i) {
int x = graph.find(parent, graph.edge[i].src);
int y = graph.find(parent, graph.edge[i].dest);
if (x == y)
return 1;
graph.Union(parent, x, y);
}
return 0;
}
// Driver Method
public static void main(String[] args) {
int V = 3, E = 3;
Graph graph = new Graph(V, E);
// add edge 0-1
graph.edge[0].src = 0;
graph.edge[0].dest = 1;
// add edge 1-2
graph.edge[1].src = 1;
graph.edge[1].dest = 2;
// add edge 0-2
graph.edge[2].src = 0;
graph.edge[2].dest = 2;
if (graph.isCycle(graph) == 1)
System.out.println("graph contains cycle");
else
System.out.println("graph doesn't contain cycle");
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100// A union by rank and path compression
// based program to detect cycle in a graph
class Graph {
int V, E;
Edge[] edge;
Graph(int nV, int nE) {
V = nV;
E = nE;
edge = new Edge[E];
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
edge[i] = new Edge();
}
}
// class to represent edge
class Edge {
int src, dest;
}
// class to represent Subset
class subset {
int parent;
int rank;
}
// A utility function to find
// set of an element i (uses
// path compression technique)
int find(subset[] subsets, int i) {
if (subsets[i].parent != i)
subsets[i].parent = find(subsets, subsets[i].parent);
return subsets[i].parent;
}
// A function that does union
// of two sets of x and y
// (uses union by rank)
void Union(subset[] subsets, int x, int y) {
int xroot = find(subsets, x);
int yroot = find(subsets, y);
if (subsets[xroot].rank < subsets[yroot].rank)
subsets[xroot].parent = yroot;
else if (subsets[yroot].rank < subsets[xroot].rank)
subsets[yroot].parent = xroot;
else {
subsets[xroot].parent = yroot;
subsets[yroot].rank++;
}
}
// The main function to check whether
// a given graph contains cycle or not
int isCycle(Graph graph) {
int V = graph.V;
int E = graph.E;
subset[] subsets = new subset[V];
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
subsets[v] = new subset();
subsets[v].parent = v;
subsets[v].rank = 0;
}
for (int e = 0; e < E; e++) {
int x = find(subsets, graph.edge[e].src);
int y = find(subsets, graph.edge[e].dest);
if (x == y)
return 1;
Union(subsets, x, y);
}
return 0;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args) {
int V = 3, E = 3;
Graph graph = new Graph(V, E);
// add edge 0-1
graph.edge[0].src = 0;
graph.edge[0].dest = 1;
// add edge 1-2
graph.edge[1].src = 1;
graph.edge[1].dest = 2;
// add edge 0-2
graph.edge[2].src = 0;
graph.edge[2].dest = 2;
if (graph.isCycle(graph) == 1)
System.out.println("Graph contains cycle");
else
System.out.println("Graph doesn't contain cycle");
}
}